Characterised by red, scaly patches on the skin, this autoimmune disease can be both physically uncomfortable and emotionally challenging. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the root causes of psoriasis, its varied symptoms, and the treatment options available
Types of Psoriasis: An Overview
Psoriasis manifests in various forms, each with unique features and challenges. Understanding these types is essential for effective management and treatment.
Plaque Psoriasis
The most common type of psoriasis is characterised by raised, red patches covered with a silvery white buildup of dead skin cells or scale. These patches commonly appear on the scalp, knees, elbows, and lower back.
Guttate Psoriasis
Often starting in childhood or young adulthood, this type appears as small, dot-like lesions. Guttate psoriasis is usually triggered by a bacterial infection, such as strep throat.
Inverse Psoriasis
Found in the body’s skin folds such as the armpits, groin, under the breasts, and around the genitals, inverse psoriasis causes smooth patches of red, inflamed skin that worsen with friction and sweating.
Pustular Psoriasis
This uncommon form of psoriasis is characterised by white pustules surrounded by red skin. It can occur in isolated patches or widespread areas.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis
The least common type of psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis, can cover your entire body with a red, peeling rash that can itch or burn intensely. It is a severe form of psoriasis that requires immediate medical attention.
Nail Psoriasis
Psoriasis can affect fingernails and toenails, causing pitting, abnormal nail growth, and discolouration. Nail psoriasis is often associated with psoriatic arthritis.
Psoriatic Arthritis
In addition to skin symptoms, psoriasis can affect the joints. Psoriatic arthritis can cause swelling, stiffness, and pain in and around the joints, leading to joint damage if left untreated.
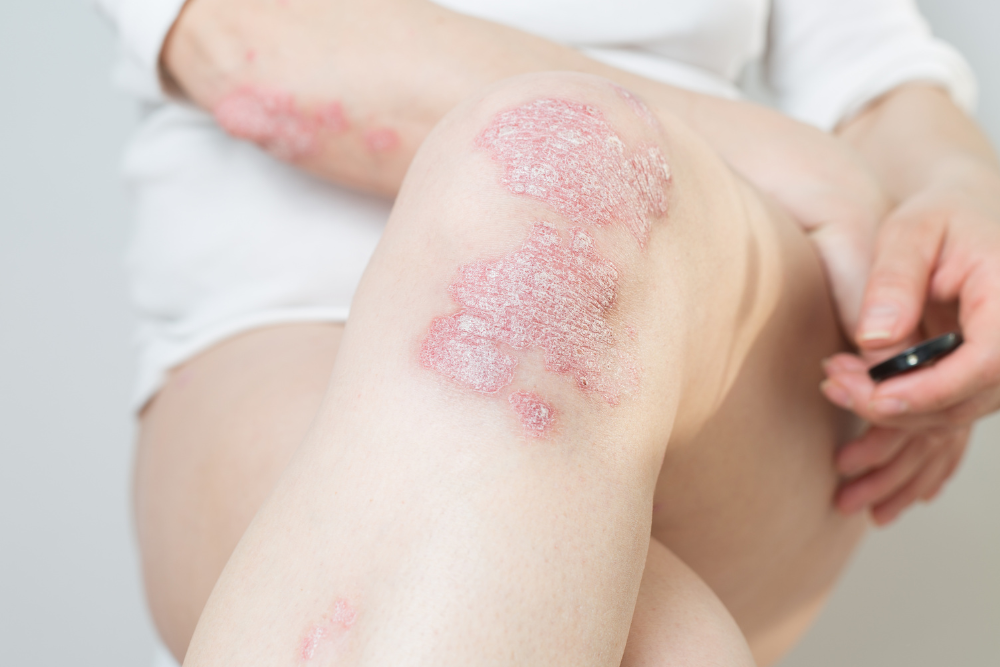
Understanding What Causes Psoriasis
The precise cause of psoriasis is not fully understood. However, it is believed to stem from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.¹ Individuals with a genetic predisposition may experience an immune system reaction to specific triggers, which can include:
Infections
Conditions like streptococcal tonsillitis, HIV, and other viral infections can prompt psoriasis flare-ups.
Stress
Severe stress is known to trigger or worsen psoriasis symptoms.
Certain lifestyle factors can also aggravate psoriasis:
Smoking and Alcohol
Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can exacerbate the condition.
Additionally, having a family history of psoriasis increases the likelihood of developing it.
Some medications are known to trigger psoriasis or make it worse. These include:
- Lithium
- Beta-Blockers
- Anti-Malarial Drugs
If you are taking corticosteroids for psoriasis, it’s important to consult with your doctor on how to gradually reduce the dosage to prevent flare-ups.
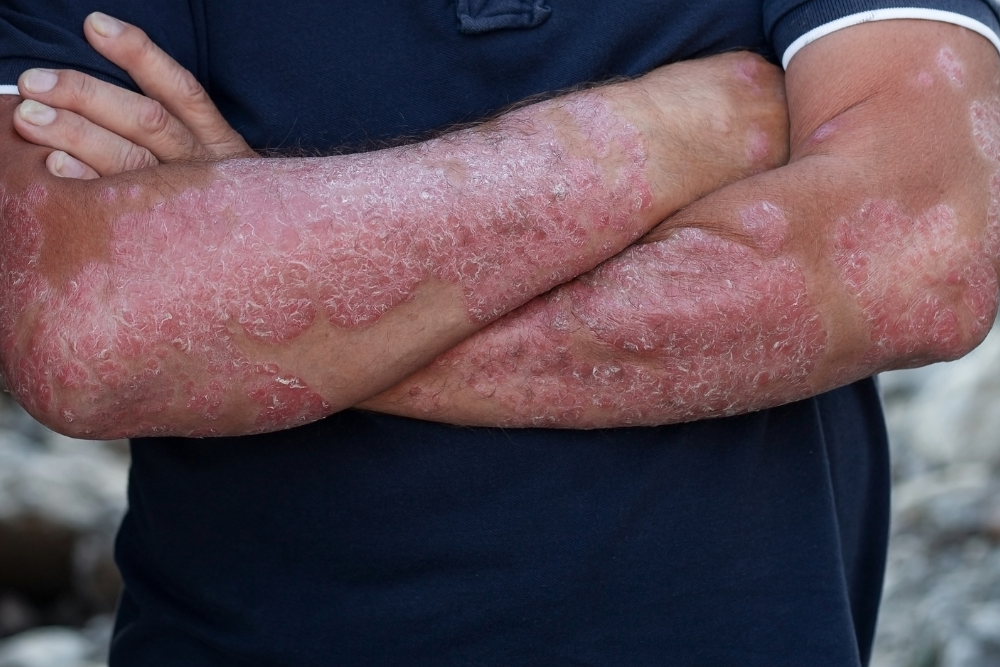
Identifying the Common Symptoms of Psoriasis
Psoriasis presents a range of symptoms that vary in severity and form. Recognising these symptoms is essential for early diagnosis and effective management. This section outlines the common symptoms associated with psoriasis, helping individuals identify the condition and seek timely medical advice.
Red, Inflamed Patches of Skin
One of the most common signs of psoriasis is raised areas of inflamed skin, which are often red on white skin and may appear darker on darker skin tones.¹
Silvery-White Scales
These patches are typically covered with a layer of silvery-white scales, which are dead skin cells that have built up due to the rapid turnover of cells caused by psoriasis.¹
Dry Skin
The affected skin may be so dry that it cracks and bleeds. In some cases, the dryness can extend beyond the patches themselves.¹
Thickened, Pitted, or Ridged Nails
Psoriasis can also affect the nails, leading to abnormalities like pitting, thickening, and irregular nail growth.¹
Joint Pain and Swelling
In the case of psoriatic arthritis, individuals may experience joint pain and swelling, which can range from mild to severe.¹
Psoriasis symptoms can vary greatly from person to person, and not everyone will experience all these symptoms. Plus, the severity and extent of symptoms can fluctuate over time, with periods of psoriasis flare-ups and remission. If you suspect you may have psoriasis, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
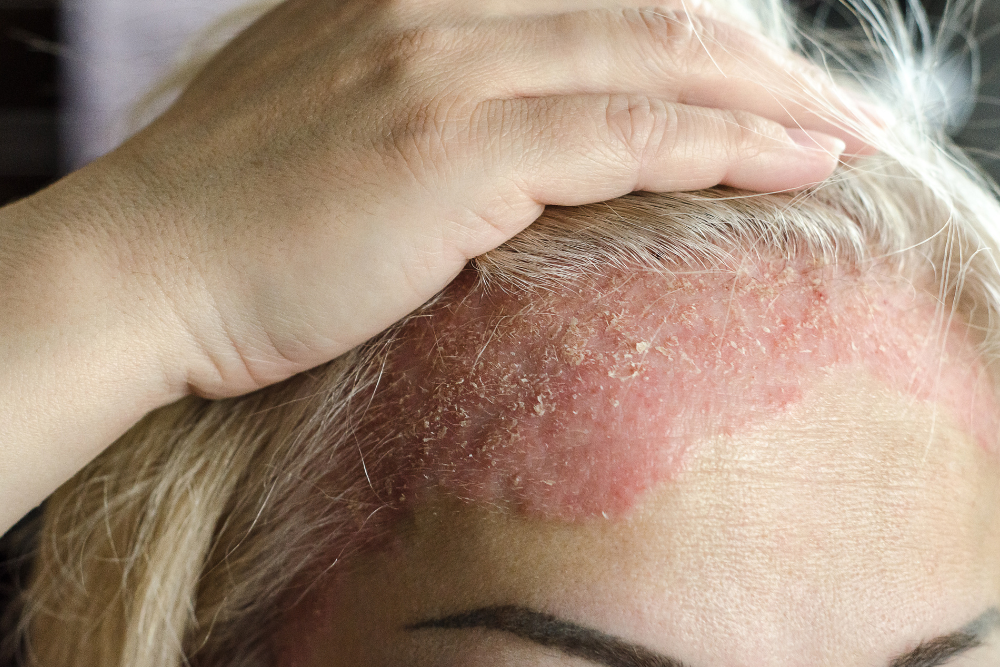
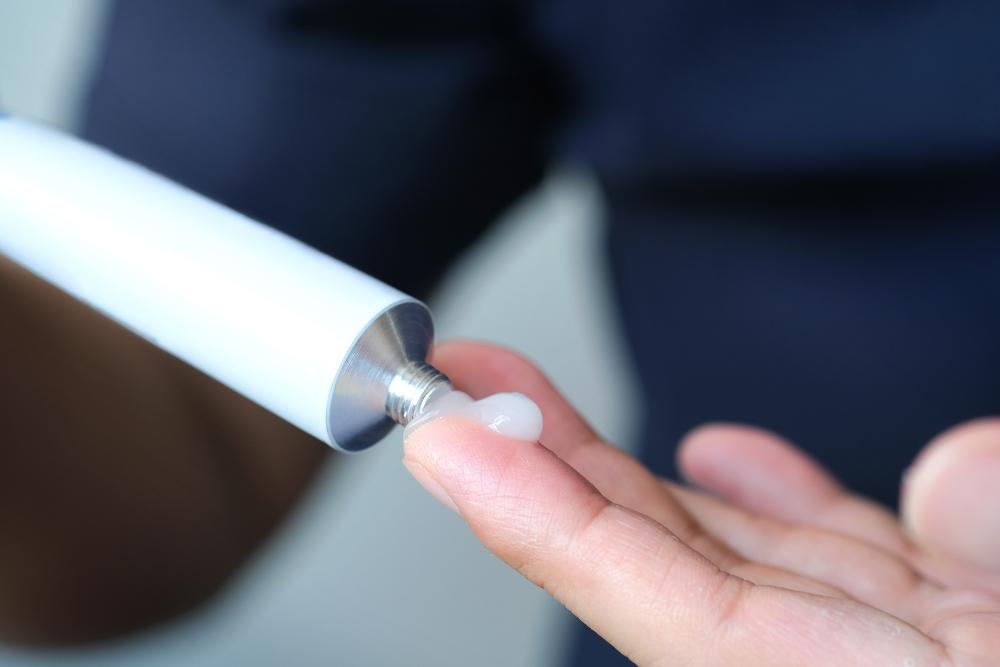
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
While there is no cure for psoriasis, numerous treatments are available to help control the condition and reduce flare-ups. Managing psoriasis often requires ongoing treatment throughout a person’s life.¹
There are three main approaches to treating psoriasis: topical treatments, light therapy, and systemic (whole body) treatments.
Topical Treatments
These are applied directly to the skin as creams or ointments:
- Corticosteroids
- Calcipotriol (a form of vitamin D)
- Tazarotene (a type of retinoid)
- Coal Tar
Light Therapy
Light therapy includes methods such as ultraviolet (UV) phototherapy and photochemotherapy.
Systemic Treatments
Systemic treatments involve medications that affect the whole body and may include:
- Retinoids
- Biological Medicines (derived from natural sources like microorganisms, plants, animals, and humans)
General Management Tips
In addition to these treatments, there are general strategies to help manage psoriasis:
- Moisturise regularly
- Follow prescribed treatment instructions as prescribed
- Reduce stress
- Maintain a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle
- Avoid Smoking
- Limit alcohol¹
It’s important to work closely with healthcare professionals to find the most suitable psoriasis treatment plan. The effectiveness of treatments can vary, and what works for one person might not work for another. Regular monitoring and adjustments are often necessary to effectively manage psoriasis.

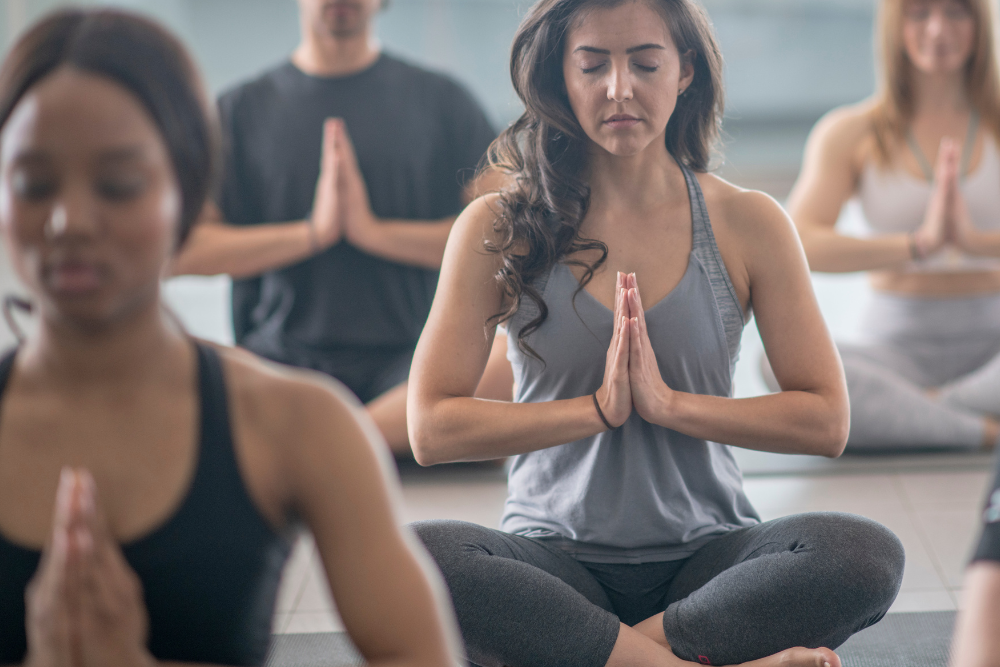
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Psoriasis Flare-ups
Living with a psoriasis diagnosis often requires more than just medical treatments; lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing the condition. Implementing certain habits and adjustments can help reduce the occurrence of flare-ups and improve overall well-being. In this section, we explore practical lifestyle changes that can benefit individuals with psoriasis:
Stress Management
Stress is a known trigger for psoriasis flare-ups. Meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help manage stress levels.
Balanced Diet
While there’s no specific ‘psoriasis diet,’ eating a balanced, nutritious diet can support overall health and potentially impact psoriasis. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, may help reduce inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, are also beneficial.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the severity of psoriasis and improve the effectiveness of treatments. Regular exercise and a balanced diet contribute to weight management.
Avoiding Alcohol and Smoking
Alcohol and tobacco use can both trigger psoriasis flare-ups. Reducing alcohol consumption or quitting smoking can help in managing the condition more effectively.
Skincare Routine
Gentle daily skincare can soothe psoriasis and reduce dryness, itching, and scaling. This includes using fragrance-free moisturisers, taking lukewarm baths with mild soaps, and avoiding harsh skin products.
Sun Exposure
Moderate sun exposure can improve psoriasis symptoms due to the natural UV light. However, it’s crucial to avoid sunburn, which can worsen psoriasis, by using sunscreen on unaffected areas.
Avoiding Certain Medications
Some medications can exacerbate psoriasis. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider about the potential effects of current medications on psoriasis.
Regular Health Check-ups
Regular check-ups are important, as individuals with psoriasis have an increased risk of other health conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and depression.
Community and Support
Joining a psoriasis support group in person or online can provide emotional support, practical tips, and a sense of community.
While lifestyle changes alone cannot cure psoriasis, they can significantly aid in managing the condition and improving quality of life. Discussing these changes with a healthcare provider is always recommended to ensure they complement your overall treatment plan.

Coping Strategies for Living with Psoriasis
Living with psoriasis can be challenging, but developing effective coping strategies can significantly improve the quality of life. Managing psoriasis goes beyond medical treatments; it involves adopting practices that help mitigate the physical discomfort and emotional stress associated with the condition. Here are some key coping strategies for living with psoriasis:
Stay Informed: Educate yourself about psoriasis. Understanding your condition can help you manage it better and communicate effectively with your healthcare providers.
Follow Treatment Plans: Adhere to the treatment regimen prescribed by your doctor. Consistency is key in managing symptoms and preventing flare-ups.
Skin Care Routine: Develop a daily skincare routine to keep your skin moisturised. Use gentle, fragrance-free products to reduce irritation and dryness.
Stress Management: Since stress can trigger psoriasis flare-ups, incorporate stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises into your routine.
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep. Avoiding alcohol and smoking can also help reduce flare-ups.
Seek Support: Connect with others who have psoriasis. Support groups, whether online or in person, can provide valuable advice, empathy, and a sense of community.
Dress Comfortably: Wear soft, breathable clothing to avoid irritating your skin. Avoid tight or rough materials that can cause discomfort.
Mindful Exposure to Sunlight: While moderate sun exposure can improve symptoms, too much sun can worsen them and increase the risk of skin cancer. Always use sunscreen on unaffected areas.
Manage Coexisting Conditions: Be vigilant about related health issues like psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and depression. Regular check-ups and a holistic approach to health are important.
Remember, coping with psoriasis is a personal journey, and what works for one person may not work for another. It’s important to find what helps you individually and to seek support from healthcare professionals when needed.
Manage psoriasis with hub.health – order treatments online and get them delivered to your door!
Sources
- Healthdirect. Psoriasis [Internet]. Healthdirect; 2024 [cited 2024 Jun 14]. Available from: https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/psoriasis#symptoms





