Are you wondering ‘where can I get birth control pills’? Well, you have several options: directly from your doctor, via telehealth platforms like hub.health, or at sexual health clinics. This guide offers you a clear rundown of each avenue to acquiring birth control pills, providing trusted advice to ensure your experience is as straightforward as possible.
Key Takeaways
-
Birth control pills require a prescription, which can be obtained via in-person doctor visits, telehealth consultations, or sexual health clinics, depending on individual health profiles and personal circumstances.
-
Once prescribed, birth control pills can be purchased from various places, including local pharmacies, family planning clinics, and via home delivery from digital pharmacies.
-
The cost of birth control pills varies by insurance coverage, government programs like the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) in Australia, and whether generic versions are available, with prices typically ranging from $0 to $50 per month.
Obtaining a Prescription for Birth Control Pills

The journey of acquiring birth control begins with a prescription from a healthcare professional. This starts with an assessment of your medical and family history, which guides the prescription of suitable birth control pills. Keep in mind, birth control pills are most suitable for women who can maintain a daily pill-taking schedule and seek reliable protection against pregnancy.
Maintaining regular communication with your healthcare provider is particularly important if you’re under 18 or over 35, as it allows for adjustments to your contraceptive method based on your risk profiles.
Visiting a Doctor or Nurse Practitioner
The traditional way to start your birth control journey is by visiting a doctor or a nurse practitioner. They will assess your medical history and help you understand how taking the pill can fit into your lifestyle. Pharmacists can also play a role by referring individuals who require a medical assessment to their general practitioner or, in emergency situations, to the hospital.
This approach guarantees that you’re not only obtaining a prescription but also gaining insight into how birth control pills, such as the combined oral contraceptive pill and the mini pill, function in your body, plus potential side effects.
Telehealth Consultations
In today’s digital age, getting a prescription for birth control pills doesn’t necessarily require an in-person visit. Telehealth consultations offer a convenient option for obtaining birth control prescriptions remotely. From the comfort of your own home, you can:
Discuss your medical history, lifestyle, reproductive history, and preferences with a healthcare provider
Receive personalised recommendations and guidance
Get a prescription for birth control pills
Schedule follow-up appointments as needed
Telehealth platforms like hub.health even offer same-day access to emergency contraception after unprotected sex.
Sexual Health Clinics
If you’re looking for a more comprehensive approach to your sexual health, sexual health clinics may suit your needs. These clinics provide advice, consultation, and treatments for contraceptive and sexual health needs. Some clinics offer walk-in services, while others may require an appointment. These clinics often offer low-cost or free services.
However, some clinics may require a referral from a doctor to access their services. If you’re unable to make an in-person visit, many clinics also offer telehealth services for remote consultations and prescriptions.
Where to Purchase Birth Control Pills

With a prescription secured, the next step is procuring your birth control pills. But what options do you have? Pharmacies are a common place to purchase birth control pills with a prescription. However, there are other options too, such as family planning clinics and online pharmacies like hub.health. Remember, if a pharmacy is unable to provide birth control pills, the pharmacist may refer you to a doctor or another healthcare professional.
Let’s further explore these options.
Pharmacies
Pharmacies are your traditional go-to places for purchasing birth control pills. In some regions, like New South Wales (NSW), a trial allows trained pharmacists to supply a 12-month supply of certain low-risk oral contraceptive pills without a new prescription from a doctor. Pharmacists can dispense a four-month emergency supply of an oral contraceptive pill and continue a script issued by a healthcare professional for up to 12 months for low-risk pills.
Bear in mind, pharmacists can only provide a resupply of the contraceptive pill if its primary use is for contraception, rather than for other purposes, like acne.
Family Planning Clinics
Family planning clinics are specialised healthcare facilities that support a wide range of needs in the realm of reproduction, contraception, and pregnancy. They can prescribe birth control pills and offer a wider range of sexual health services, including education on various reproductive issues and the importance of understanding one’s family medical history.
With family planning clinics located in each Australian state and territory, they are widely accessible to individuals of various ages and life stages. Fees for consultations at these clinics vary, but Medicare rebates may be available for some individuals; bulk billing options may also be offered for eligible groups.
Online Pharmacies
Online healthcare platforms like hub.health offer a convenient alternative for purchasing birth control pills, ensuring continued access through community pharmacists while maintaining effective communication with doctors to ensure consistent care.
The Cost of Birth Control Pills
Now that you know where to get your pills, let’s talk about the cost. The cost of birth control pills typically ranges from $0 to $50 per month. But, the pricing can vary based on insurance coverage and government programs, as well as the type of birth control pill prescribed.
Insurance Coverage
Private health insurance plans in Australia may cover the cost of birth control pills, although coverage can vary depending on the specific insurance provider and plan. Some insurance plans may cover the full cost, while others may require a co-payment.
Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme
In Australia, some oral contraceptive pills are listed under the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS), making them cheaper than those that aren’t covered by the scheme. Brands listed under the PBS generally cost between $10 to $30 a month, with generic versions being at a lower cost. However, newer-generation pills that are not listed under the PBS can be more expensive, potentially costing upwards of $90 a month.
Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Out-of-pocket expenses for birth control pills can vary. Brand-name oral contraceptives with generic alternatives tend to have the largest share of users with annual out-of-pocket spending.
Alternative Contraceptive Methods
While we are focusing on birth control pills, it’s important to remember that they’re not the only option available. There are a variety of birth control options available including:
Implants
Intrauterine devices (IUDs)
Injections
Pills
Barrier methods
Sterilisation
Emergency contraception
Natural methods
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are small contraceptive devices inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. There are two main types of IUDs: copper IUDs and hormonal IUDs.
Both copper and hormonal IUDs are highly effective methods of contraception, remaining effective for durations ranging from 5 to 10 years depending on the type.
Contraceptive Implants
Contraceptive implants are small, flexible rods inserted under the skin of the upper arm, releasing the hormone etonogestrel to prevent pregnancy. The contraceptive implant inhibits ovulation and thickens cervical mucus to prevent sperm from entering the uterus.
In Australia, certain contraceptive implants can prevent pregnancy for up to 3 years before needing replacement.
Condoms and Barrier Methods
Condoms and barrier methods work by blocking sperm from reaching an egg. They include:
External (male) condoms
Internal (female) condoms
Diaphragms
Cervical caps
Contraceptive sponges
To maximise their efficacy, it’s essential to use barrier methods correctly and consistently, recognising that no method offers perfect protection.
Tips for Taking Birth Control Pills Effectively
Taking birth control pills effectively involves a few key strategies. These include consistent timing, handling missed pills, and being aware of interactions with other medications, especially when using combined oral contraceptive pills. It’s also important to understand the role of inactive pills in your birth control regimen.
Let’s explore each of these strategies to maximise the effectiveness of your birth control pills.
Consistent Timing
Consistent timing is integral to the effectiveness of birth control pills, especially for progestin-only pills, which must be taken within the same 3-hour window every day. Using tools such as alarms, calendar reminders, or birth control apps can help in remembering to take the pill at the same time each day.
Handling Missed Pills
Missed a birth control pill? Don’t panic, but do take action. If a combined pill is missed, the next step depends on the type of pill, the number of missed pills, and the week of the pack you’re in.
For progestin-only pills, if a pill is taken more than 3 hours past the usual time, a backup method of birth control is recommended for the next 48 hours.
Interactions with Other Medications
Taking other medications alongside your birth control pills? Be aware that certain medications and supplements can decrease the effectiveness of birth control pills, including some antibiotics, anti-seizure medications, and St. John’s Wort.
Always inform your healthcare providers about all medications and supplements you’re taking to assess the potential impact on birth control effectiveness.
Understanding the Side Effects and Risks
Although birth control pills are generally deemed safe, understanding their potential side effects and risks is important. These can range from common side effects to serious health risks, and individual factors can also affect your risk level.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects of birth control pills can include:
Headaches
Nausea
Breast tenderness
Bloating
Emotional or mood changes
Weight gain
Changes in bleeding patterns, such as breakthrough bleeding or spotting, particularly with continuous-dosing or extended-cycle pills.
Serious Health Risks
Although serious health issues associated with birth control pills are rare, being aware of them is essential. Combination pills can increase the risk of serious health issues such as:
Heart attacks
Strokes
Blood clots
Liver disorders
Smokers face a heightened risk of stroke, heart attack, or blood pressure issues when using combination birth control pills.
Individual Factors Affecting Risk
Individual factors, such as age, smoking, and medical conditions, can affect the risk associated with birth control pills. Ambivalence toward childbearing and contraception, where an individual is neither explicitly against nor in favour of pregnancy, can place them at a higher risk of unintended pregnancy.
Birth Control Pills and STD Protection
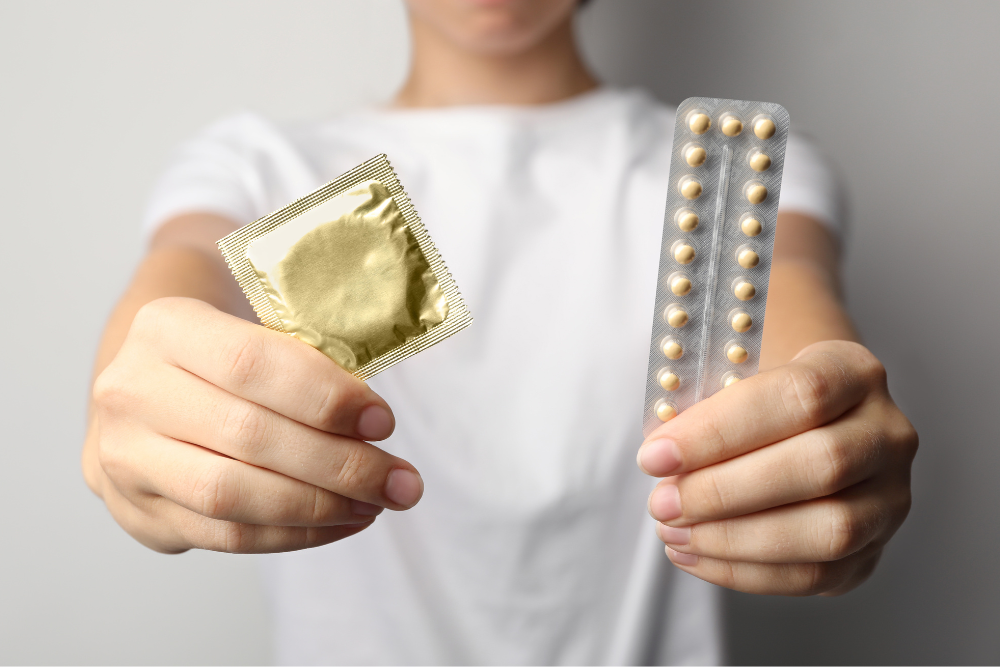

Although birth control pills efficiently prevent pregnancy, they do not offer protection against STDs and HIV. Using a latex condom correctly every time during sex is one way to lower the risk of getting an STD.
Using condoms in combination with birth control pills is a strategy that provides optimal protection against both unintended pregnancy and STDs/HIV.
Staying Informed and Communicating with Your Healthcare Provider
The effective use of birth control pills is an ongoing process, not a one-time event. This process involves regular check-ups, timely addressing of any side effects or concerns, and periodic evaluation of your contraceptive needs.
Routine Check-ups
Routine follow-up visits are vital for monitoring side effects or adverse events, which can help in the ongoing successful use of birth control pills. Interactions with healthcare providers during these check-ups may reinforce motivation and proper usage instructions, leading to more effective contraception.
Addressing Side Effects or Concerns
When using birth control pills, it’s essential to communicate any potential side effects or concerns to your healthcare provider, which can assist in informed decision-making and method selection. Important symptoms requiring immediate medical attention include:
Severe abdominal or leg pain
Vomiting
Difficulty breathing
Severe headaches
Confusion
Vision changes
Severe mood swings
Evaluating Contraceptive Needs Over Time
As your life changes, so might your contraceptive needs and preferences. It’s important to periodically re-evaluate your chosen method with a healthcare provider to ensure it continues to be the best option over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I get birth control pills over the counter?
No, you cannot get birth control pills over-the-counter, as they require a doctor’s prescription. It’s important to talk to your doctor about the best option for you and obtain a prescription before purchasing them from a pharmacy.
How do I get a prescription for birth control pills?
You can get a prescription for birth control pills by visiting a healthcare professional for an assessment or through a telehealth consultation. It’s important to consult with a professional to determine the best option for you.
How much do birth control pills cost?
The cost of birth control pills can vary from $0 to $50 per month depending on insurance coverage and government programs. It’s important to check with your healthcare provider for specific pricing.
What are some alternative contraceptive methods to birth control pills?
Consider using intrauterine devices (IUDs), contraceptive implants, or condoms and barrier methods as alternative contraceptive methods to birth control pills. These options offer effective protection against pregnancy without the need for daily medication.





